( Yeni ) – There are some organs in the body that may have to be “removed” due to illness or some reasons, but it will not affect too much activity and longevity, is this true?
Studies have shown that the human body has a total of 36 organs that maintain vital activities, of which the following 8 organs, even if “removed”, do not pose a danger to life:
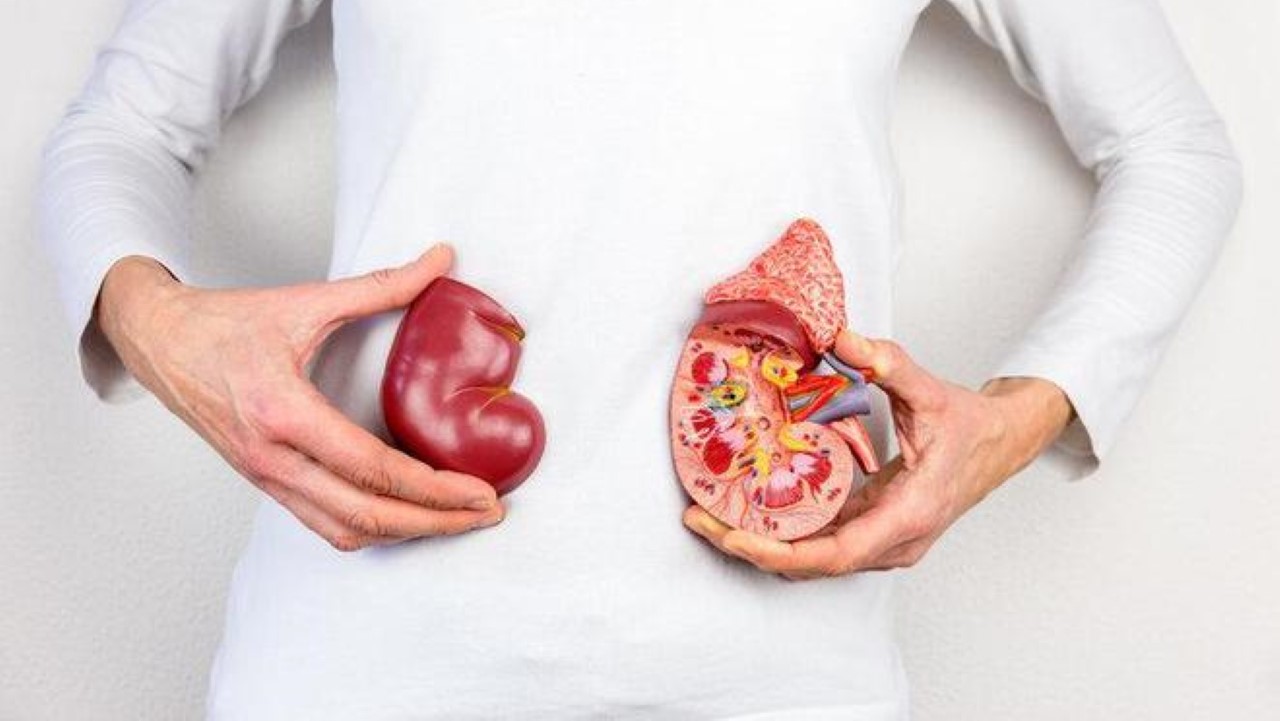
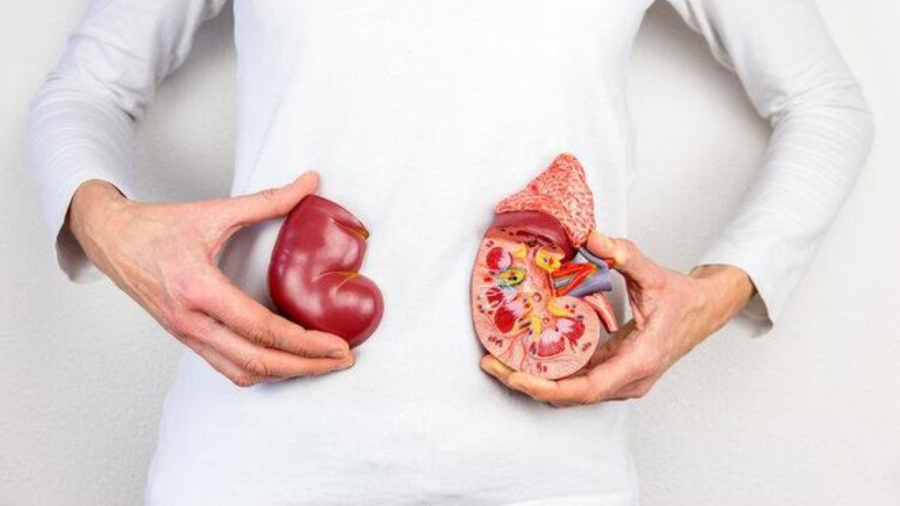
1. One kidney
The normal human body has two kidneys, and these two compensate for each other. Therefore, in special cases, after losing one kidney, the remaining healthy kidney will continue to complete the filtering function and will not greatly affect daily life.
After removing a kidney, it will not greatly affect daily life. (Illustration)
2. One lung
Like the kidneys, the human body normally relies on the left and right lungs to breathe. If the left and right lungs are completely removed, the patient will lose respiratory function. For a simultaneous heart-lung transplant, part of the lung may be removed, and it may also be transplanted.
3. Reproductive organs
Severe damage to the uterus, ovaries, breasts in women, or testicles in men may require removal. After these organs are removed, the patient can still live a normal life, but cannot fulfill his or her reproductive needs.
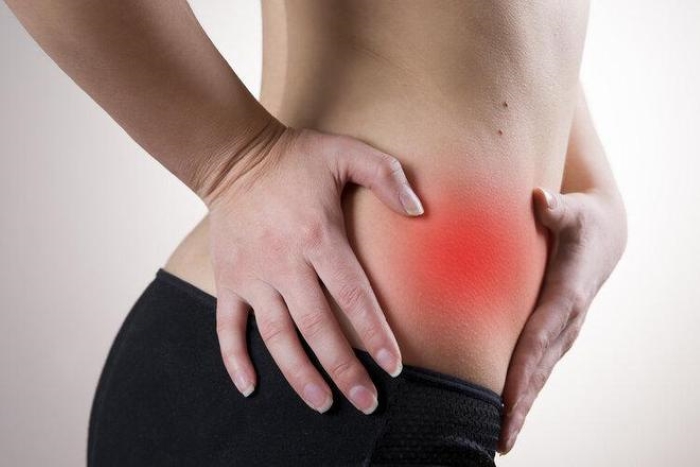
4. Appendix
Located in the lower right abdomen of the human body, it is a small tail protruding from the thickest cecum in the intestine. Appendicitis is a relatively common case and is applied with the “let it go” method. After the patient recovers, it will not affect much of daily life.
However, some studies have found that the appendix is not a useless organ, it can ensure the safety of “good bacteria” in the human body.
Appendicectomy after recovery will not affect daily activities much. (Illustration)
5. Gallbladder
The gallbladder is the organ that stores bile. If the body eats too much oil, it can use bile to break down food. After gallbladder removal, some people’s digestive function may be affected, but if they have a moderate diet, it will not affect their daily activities much.
6. Wisdom teeth
Wisdom teeth are the third molars in the human mouth, appearing relatively late and mostly concentrated in the 16-26 age group. From a medical point of view, current wisdom teeth do more harm than good. If there are cavities, impacted teeth, periodontitis, or misaligned wisdom teeth, they should be removed.
7. Spleen
The spleen primarily filters blood, but when the spleen is damaged beyond repair, it must be removed. Although ablation can affect the immune system as well as the hematopoietic system. However, in general, patients can live the same life as they did before surgery after splenectomy.
8. Stomach
The stomach is a very important organ, but for some people with severe obesity and stomach cancer, doctors may have to remove part or all of their stomach. After removal, the esophagus is connected directly to the small intestine to replace the stomach, and the patient can still eat small amounts of solid food.
***
Note: Although the body can still function every day after removing these organs, they can only be “removed” under the advice of a doctor, unless there are health problems and these parts must be removed to be “processed”.
[yeni-source src=”https://www.giaitri.thoibaovhnt.com.vn/co-8-co-quan-trong-co-the-con-nguoi-du-bi-cat-bo-cung-khong -anh-huong-den-tinh-mang-805390.html” alt_src=”https://phunutoday.vn/co-8-co-quan-trong-co-the-con-nguoi-du-bi-cat- bo-cung-not-anh-huong-den-tinh-mang-d407844.html” name=”giaitri.thoibaovhnt.vn”]